thecodingmachine / dbal-fluid-schema-builder
使用 Doctrine DBAL 和流式语法构建和修改您的数据库模式。
Requires
- php: ^7.4 || ^8.0
- doctrine/dbal: ^3.0
- doctrine/inflector: ^1.4 || ^2.0
Requires (Dev)
- php-coveralls/php-coveralls: ^2.7.0
- phpunit/phpunit: ^10.2
README
Doctrine DBAL 的流式模式构建器
使用 DBAL 和流式语法构建和修改您的数据库模式。
为什么选择它?
Doctrine DBAL 提供了一个强大的 API 来更改您的数据库模式。这个库是围绕 DBAL 标准 API 的包装器,为日常使用提供了更简短、更快速的语法。它提供了快捷方式和语法糖,以提高您的效率。
IDE 友好
您可以使用您喜欢的 IDE(PHPStorm、Eclipse PDT、Netbeans...)的自动完成功能轻松构建模式。再也不需要查看文档了!
静态代码分析
您最喜欢的静态 PHP 代码分析器(Scrutinizer、PHPStan...)可以帮您捕获错误!例如,每个数据库类型都是一个 PHP 方法,因此不再会有列类型的错误 - ... 是 'INT' 还是 'INTEGER'? :)
为什么不呢?
流式模式构建器旨在以简洁的方式解决您在 99% 的模式中遇到的情况。它不涵盖所有可能的使用情况,也没有旨在实现该目标的计划。
例如,如果您在多个列上有外键,您不能使用 FluidSchema。您应该回退到经典的 DBAL。
与 DBAL "原生" API 的比较
而不是
$table = $schema->createTable('posts'); $table->addColumn('id', 'integer'); $table->addColumn('description', 'string', [ 'length' => 50, 'notnull' => false, ]); $table->addColumn('user_id', 'integer'); $table->setPrimaryKey(['id']); $table->addForeignKeyConstraint('users', ['user_id'], ['id']);
您写下
$db = new FluidSchema($schema); $posts = $db->table('posts'); $posts->id() // Let's create a default autoincremented ID column ->column('description')->string(50)->null() // Let's create a 'description' column ->column('user_id')->references('users'); // Let's create a foreign key. // We only specify the table name. // FluidSchema infers the column type and the "remote" column.
特性
FluidSchema 尽可能使您的生活变得更简单。
表和列类型
$table = $db->table('foo'); // Supported types $table->column('xxxx')->string(50) // VARCHAR(50) ->column('xxxx')->integer() ->column('xxxx')->float() ->column('xxxx')->text() // Long string ->column('xxxx')->boolean() ->column('xxxx')->smallInt() ->column('xxxx')->bigInt() ->column('xxxx')->decimal(10, 2) // DECIMAL(10, 2) ->column('xxxx')->guid() ->column('xxxx')->binary(255) ->column('xxxx')->blob() // Long binary ->column('xxxx')->date() ->column('xxxx')->datetime() ->column('xxxx')->datetimeTz() ->column('xxxx')->time() ->column('xxxx')->dateImmutable() // From Doctrine DBAL 2.6+ ->column('xxxx')->datetimeImmutable() // From Doctrine DBAL 2.6+ ->column('xxxx')->datetimeTzImmutable() // From Doctrine DBAL 2.6+ ->column('xxxx')->timeImmutable() // From Doctrine DBAL 2.6+ ->column('xxxx')->dateInterval() // From Doctrine DBAL 2.6+ ->column('xxxx')->array() ->column('xxxx')->simpleArray() ->column('xxxx')->json() // From Doctrine DBAL 2.6+ ->column('xxxx')->jsonArray() // Deprecated in Doctrine DBAL 2.6+ ->column('xxxx')->object(); // Serialized PHP object
快捷方法
// Create an 'id' primary key that is an autoincremented integer $table->id(); // Don't like autincrements? No problem! // Create an 'uuid' primary key that is of the DBAL 'guid' type $table->uuid(); // Create "created_at" and "updated_at" columns $table->timestamps();
创建索引
// Directly on a column: $table->column('login')->string(50)->index(); // Or on the table object (if there are several columns to add to an index): $table->index(['category1', 'category2']);
创建唯一索引
// Directly on a column: $table->column('login')->string(50)->unique(); // Or on the table object (if there are several columns to add to the constraint): $table->unique(['login', 'status']);
使列可空
$table->column('description')->string(50)->null();
设置列的默认值
$table->column('enabled')->bool()->default(true);
创建外键
$table->column('country_id')->references('countries');
注意:外键将在 "countries" 表的主表上自动创建。 "country_id" 列的类型将与 "countries" 表的主键类型完全相同。
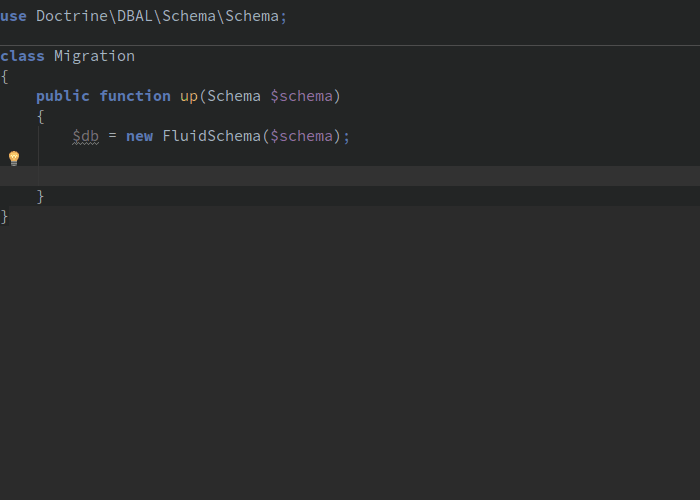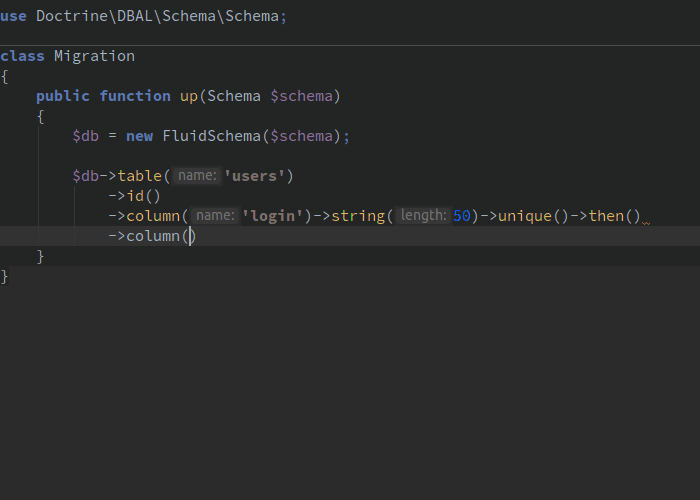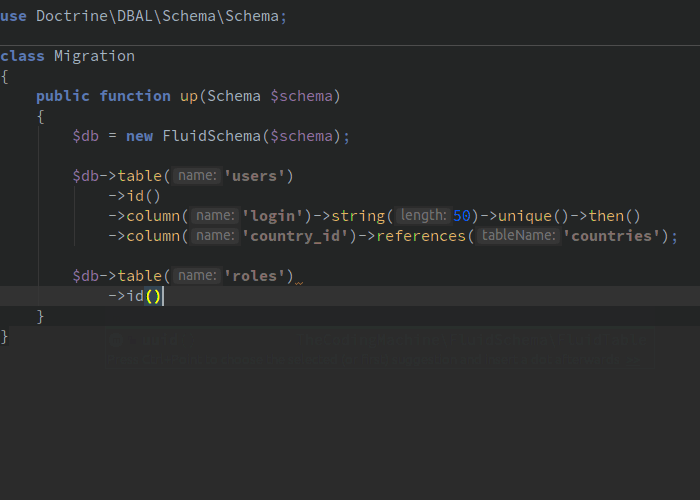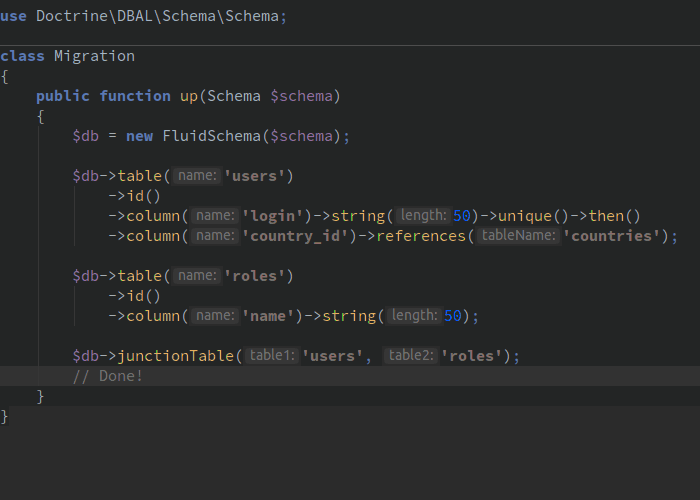
在两个表之间创建联合表(也称为关联表)
$db->junctionTable('users', 'roles'); // This will create a 'users_roles' table with 2 foreign keys: // - 'user_id' pointing on the PK of 'users' // - 'role_id' pointing on the PK of 'roles'
给列添加注释
$table->column('description')->string(50)->comment('Lorem ipsum');
声明主键
$table->column('uuid')->string(36)->primaryKey(); // or $table->column('uuid')->then() ->primaryKey(['uuid']);
在两个表之间声明继承关系
在 SQL 中,没有与 PHP 对象中相同的 "继承" 概念。然而,建模继承的常见方法是编写一个用于基类的表(包含基列/属性),然后为每个扩展类编写一个表,包含额外的列/属性。每个扩展表都有一个 既是主键也是外键,指向基表 的主键。
$db->table('contacts') ->id() ->column('email')->string(50); $db->table('users') ->extends('contacts') ->column('password')->string(50);
使用 extends 方法将自动创建一个与扩展表具有相同名称和类型的 primary key。它还将确保这个 primary key 是一个指向扩展表的外键。
自动对表和列名称进行引号处理
默认情况下,流体模式构建器 不会 引用您的标识符(因为它不知道您使用的是哪种数据库)。
这意味着您不能创建具有保留关键字的项。
$db->table('contacts') ->id() ->column('date')->datetime(); // Will most likely fail, because "date" is a reserved keyword!
然而,如果您在构建时向 流体模式构建器 提供您的数据库平台,则它将 默认引用所有标识符。不再有令人不快的惊喜!
use TheCodingMachine\FluidSchema\DefaultNamingStrategy; // Assuming $connection is your DBAL connection $db = new FluidSchema($schema, new DefaultNamingStrategy($connection->getDatabasePlatform()));