webelightdev / eager-join
此包引入了eloquent关系中的排序和过滤的连接能力。
Requires
- illuminate/database: 5.6.*
Requires (Dev)
- orchestra/testbench: ~3.6.0
- phpunit/phpunit: ^7.0
This package is auto-updated.
Last update: 2024-09-17 00:32:57 UTC
README
Laravel Eloquent Join
此包引入了eloquent关系中的排序和过滤的连接能力。
Eloquent问题
你无法在不手动连接相关表的情况下对关系字段进行排序,这非常不方便。让我给你几个原因。如果你有一个包含帖子及其相关类别的表,你的代码可能看起来像这样
$posts = Post::select('posts.*')
->join('categories', 'categories.id', '=', 'posts.category_id')
->groupBy('posts.id')
->where('categories.deleted_at', '=', null)
->orderBy('categories.name');
if(request()->get('date')){
$posts->where('posts.date', $date)
}
$posts = $posts->get();
1.第一个问题是你需要担心选择(select)。
->select('posts.*')
原因:如果不使用select(),则可以从category中选择id并将其注入到Post模型中。
2.第二个问题是你需要担心groupBy。
->groupBy('posts.id');
原因:如果关系是HasOne,并且帖子有多个类别,则查询将返回更多行。
3.第三个问题是你需要将所有其他where子句从
->where('date', $date)
改为
->where('posts.date', $date)
原因:post和category可以有"date"属性,在这种情况下,如果不选择具有表"模糊列"的属性,将会抛出错误。
4.第四个问题是你在使用表名(而不是模型)并且这也很糟糕和尴尬。
->where('posts.date', $date)
5.第五个问题是你需要担心连接表的软删除。如果类别使用SoftDeletes特性,你必须添加
->where('categories.deleted_at', '=', null)
此包将为您自动解决上述所有问题。您可以在不连接的情况下对关系字段进行过滤,但此包将提供更轻松执行此操作的能力。
版本兼容性
安装
1.使用composer安装包
composer require fico7489/laravel-eloquent-join:"*"
使用此语句,composer将为您的当前laravel版本安装最高版本的包。
2.在您的基模型或特定模型中使用Fico7489\Laravel\EloquentJoin\Traits\EloquentJoinTrait特性。
...
use Fico7489\Laravel\EloquentJoin\Traits\EloquentJoinTrait;
use Illuminate\Database\Eloquent\Model;
abstract class BaseModel extends Model
{
use EloquentJoinTrait;
...
就这样,你可以开始了。
选项
使用表别名
我们应该为连接表使用别名吗(默认为false)
使用true时查询将如下所示
select "sellers".* from "sellers"
left join "locations" as "5b5c093d2e00f"
on "5b5c093d2e00f"."seller_id" = "sellers"."id" and "5b5c093d2e00f"."is_primary" = ?
and "5b5c093d2e00f"."is_secondary" = ?
and "5b5c093d2e00f"."deleted_at" is null
group by "sellers"."id" order by "5b5c093d2e00f"."id" desc
使用false时查询将如下所示
select "sellers".* from "sellers" left join "locations"
on "locations"."seller_id" = "sellers"."id"
and "locations"."is_primary" = ?
and "locations"."is_secondary" = ?
and "locations"."deleted_at" is null
group by "sellers"."id" order by "locations"."id" desc
在您的基模型中设置选项
public function __construct(array $attributes = [])
{
parent::__construct($attributes);
$this->useTableAlias = true;
}
使用说明
目前可用于连接查询的关系
- BelongsTo
- HasOne.
在BelongsTo和HasOne关系上为eloquent构建器添加新子句
- orderByJoin($column, $sortBy = 'asc') $sortBy参数与默认eloquent sortBy()相同
- whereJoin($column, $operator = null, $value = null, $boolean = 'and') $operator、$value、$boolean参数与默认eloquent where()相同
- orWhereJoin($column, $operator = null, $value) $operator和$value参数与默认eloquent orWhere()相同
whereJoin、orElseJoin和orderByJoin中列参数的规则
- 当前表属性
- 相关表属性(使用点分隔的关系名称)
- 相关表可以无限嵌套,使用HasOne和BelongsTo关系的任何组合,它们只需满足连接查询的关系规则即可。
->where('title', '=', 'test')
->where('relationName.title', '=', 'test')
->where('relationName.relationNameSecond.title', '=', 'test')
可以在查询上使用连接子句的BelongsTo和HasOne关系
- 您想用于连接查询的关系只能有这些子句:where、orWhere、withTrashed、onlyTrashed、withoutTrashed。
- where和orWhere子句只能有这种变化:->where($columnn, $operator, $attribute),不允许使用闭包。
- 不允许使用whereHas、orderBy等其他子句。
- 您可以在关系上添加不允许的条款并按正常优雅的方式使用它们,但在此情况下,您不能使用这些关系进行连接查询。
- 如果对使用SoftDeletes的关系模式未应用
withTrashed、onlyTrashed或withoutTrashed,则默认行为为withoutTrashed,这意味着连接查询将默认仅查找未软删除的相关表。
允许的关系
public function locationPrimary()
{
return $this->hasOne(Location::class)
->where('is_primary', '=', 1)
->orWhere('is_primary', '=', 1)
->withTrashed();
}
不允许的关系
public function locationPrimary()
{
return $this->hasOne(Location::class)
->where('is_primary', '=', 1)
->orWhere('is_primary', '=', 1)
->withTrashed()
->whereHas('state', function($query){return $query;}
->orderBy('name');
}
第二个关系不允许的原因是,这个包在左连接上应用了where、orWhere等条款(所有优雅的条款都不能在连接上执行)。Eloquent可以使用所有这些条款,因为Eloquent使用子查询而不是连接。
其他
- 您可以无限次地组合新的条款
- 如果您在同一个关系包上多次组合条款,则相关表将只连接一次
- 您可以将连接条款(例如whereJoin())与优雅条款(例如orderBy())组合
Seller::whereJoin('title', 'test')->whereJoin('city.title', 'test')->orderByJoin('city.title')->get();
您可能会觉得有许多规则和限制,但实际上并非如此。不用担心,如果您创建了不允许的查询,将抛出EloquentJoinException异常,并解释发生了什么。
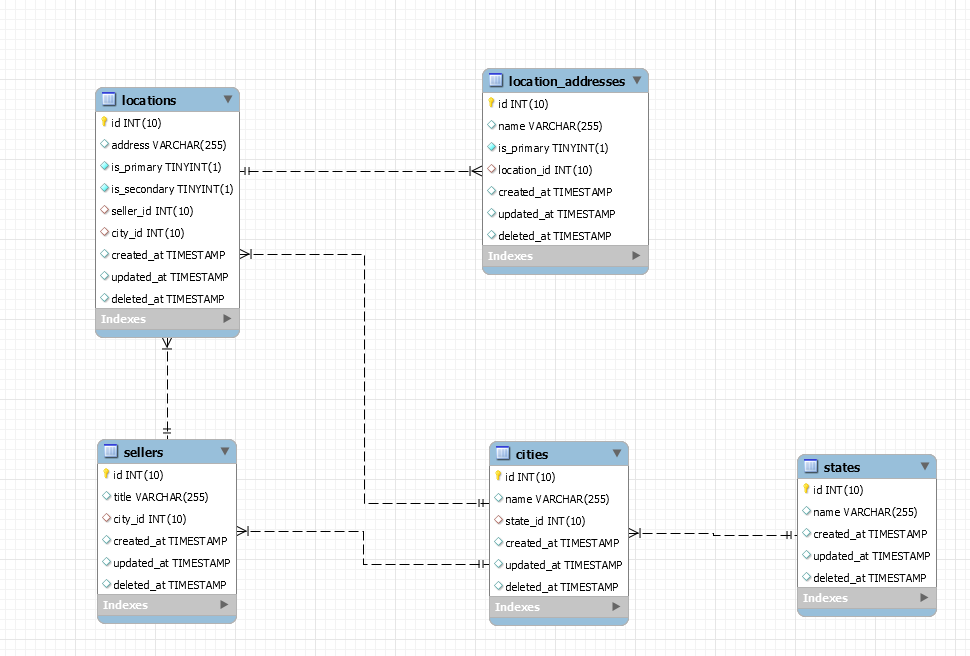
查看真实示例中的操作
数据库模式
模型
class Seller extends BaseModel
{
public function locationPrimary()
{
return $this->hasOne(Location::class)
->where('is_primary', '=', 1);
}
public function city()
{
return $this->belongsTo(City::class);
}
class Location extends BaseModel
{
public function locationAddressPrimary()
{
return $this->hasOne(LocationAddress::class)
->where('is_primary', '=', 1);
}
class LocationAddress extends BaseModel
{
class City extends BaseModel
{
public function state()
{
return $this->belongsTo(State::class);
}
}
class State extends BaseModel
{
排序
按卖家标题排序卖家
Seller::orderByJoin('title')
按城市名称排序卖家
Seller::orderByJoin('city.title')
按州名称排序卖家
Seller::orderByJoin('city.state.title')
按主要位置地址排序卖家
Seller::orderByJoin('locationPrimary.address')
按主要位置的位置地址名称排序卖家
Seller::orderByJoin('locationPrimary.locationAddressPrimary.address')
您也可以多次组合orderBy
Seller::orderByJoin('title')->orderBy('city.title')
过滤
过滤标题为'test'的卖家
Seller::whereJoin('title', 'test')
过滤城市名称为'test'的卖家
Seller::whereJoin('city.title', '=', 'test')
过滤州名称为'test'的卖家
Seller::whereJoin('city.state.title', '=', 'test')
过滤主要位置地址为'test'的卖家
Seller::whereJoin('locationPrimary.address', '=', 'test')
过滤主要位置的位置地址名称为'test'的卖家
Seller::whereJoin('locationPrimary.locationAddressPrimary.address', '=', 'test')
您也可以多次组合orderBy
Seller::whereJoin('title', 'test')->whereJoin('city.title', 'test')
现在让我们看看文档中的第一个示例现在是什么样子。这段代码
$posts = Post::select('posts.*')
->join('categories', 'categories.id', '=', 'posts.category_id')
->groupBy('posts.id')
->where('categories.deleted_at', '=', null)
->orderBy('categories.name');
if(request()->get('date')){
$posts->where('posts.date', $date)
}
$posts = $posts->get();
现在是
$posts = Post::orderByJoin('category.name');
if(request()->get('date')){
$posts->where('posts.date', $date)
}
$posts = $posts->get();
这两个代码片段生成相同的MySQL查询。
测试
这个包有很好的测试覆盖。如果您想运行测试,只需运行composer update,然后运行测试:"vendor/bin/phpunit"
贡献
请随时创建有关
- 错误
- 通知
- 请求新功能
- 问题
- 澄清
- 等...
许可证
MIT
自由软件,太棒了!