tarsana / command
一个用于构建命令行应用程序并与世界共享的框架
Requires
- php: >=7.3
- tarsana/io: ^2.0
- tarsana/syntax: ^2.0
- twig/twig: ^2.4
Requires (Dev)
- phpunit/phpunit: ^9.3
This package is auto-updated.
Last update: 2024-08-29 03:57:18 UTC
README
一个用于使用PHP构建命令行应用程序的库。这是Tarsana项目的一部分。
目录
-
交互式读取参数和选项 自版本1.1.0起
-
加载配置 新版本1.2.0
安装
使用Composer安装它
composer require tarsana/command
您的第一个命令
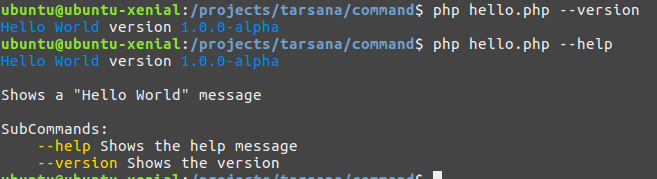
让我们编写一个“Hello World”命令。创建一个名为hello.php的文件,内容如下
<?php require __DIR__.'/vendor/autoload.php'; use Tarsana\Command\Command; class HelloWorld extends Command { protected function execute() { $this->console->line('Hello World'); } } (new HelloWorld)->run();
然后从终端运行它
$ php hello.php
Hello World
恭喜你,你刚刚编写了你的第一个命令 :D
正如你所见,Tarsana\Command\Command是一个提供命令基本功能的类。每个命令都应该扩展它并实现execute()方法。
初始化命令
此外,Command还提供了init()方法,用于初始化命令的一般属性。让我们重新编写我们的HelloWorld命令
class HelloWorld extends Command { protected function init () { $this->name('Hello World') ->version('1.0.0-alpha') ->description('Shows a "Hello World" message'); } protected function execute() { $this->console->line('Hello World'); } }
这里我们覆盖了init()方法来定义命令的名称、版本和描述。
请注意,属性foo的设置器命名为foo()而不是setFoo()。我知道这并不是一个常见的约定,但对我来说这是有意义的。 :P
$this->name('blabla'); // will set the name to 'blabla' and return $this $this->name(); // calling it without parameter will get the value of name
显示命令的帮助和版本
要显示命令的版本,我们使用--version标志(我们将在之后了解这实际上是一个子命令)。我们还有--help来显示帮助信息
读取和写入控制台
属性console用于处理对控制台的读取和写入操作。
让我们更新我们的命令以读取用户名
protected function execute() { $this->console->out('Your name: '); $name = $this->console->readLine(); $this->console->line("Hello {$name}"); }
$ php hello.php
Your name: Amine
Hello Amine
readLine()方法从stdin读取一行并返回它作为字符串。out()方法将一些文本写入stdout(不带换行符)。line()方法将一些文本写入stdout并添加换行符。error()方法将一些文本写入stderr并添加换行符。
Console类提供了一些标签来控制输出
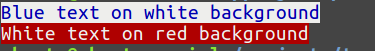
$this->console->line('<background:15><color:19>Blue text on white background<reset>'); $this->console->line('<background:124><color:15>White text on red background<reset>');
<background:$number>和<color:$number>标签允许设置要写入的文本的背景和前景颜色;<reset>标签重置默认值。颜色以256色模式中的数字表示。
支持的标签列表
<color:$n>:将前景文本设置为256色模式中的颜色$n。<background:$n>:将前景文本设置为256色模式中的颜色$n。<reset>:重置格式化默认值。<bold>:使文本加粗。<underline>:下划线文本。
Console还允许您使用别名定义样式
$this->console->alias('<danger>', '<background:124><color:15><bold>'); $this->console->alias('</danger>', '<reset>'); $this->console->line('<danger>Some text</danger>'); // is equivalent to $this->console->line('<background:124><color:15><bold>Some text<reset>');
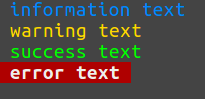
预定义别名有
$this->console->line('<info> information text </info>'); $this->console->line('<warn> warning text </warn>'); $this->console->line('<success> success text </success>'); $this->console->line('<error> error text </error>'); $this->console->line('<tab>'); // prints four spaces " " $this->console->line('<br>'); // prints line break PHP_EOL
注意:可以在打印到控制台的所有字符串中使用标签和别名,包括命令和参数描述。
定义参数和选项
命令语法是通过使用Syntax库定义的。让我们从一个重复单词多次的命令开始
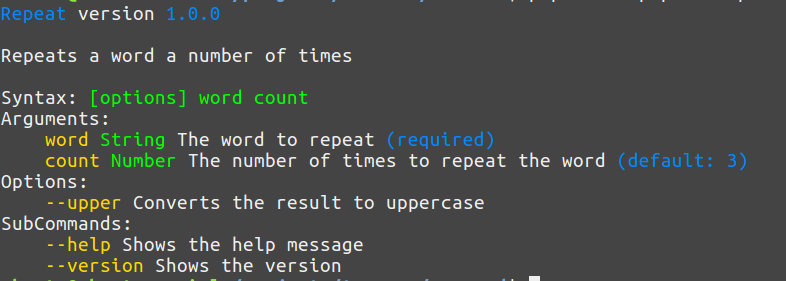
class RepeatCommand extends Command { protected function init () { $this->name('Repeat') ->version('1.0.0') ->description('Repeats a word a number of times') ->syntax('word: string, count: (number: 3)') ->options(['--upper']) ->describe('word', 'The word to repeat') ->describe('count', 'The number of times to repeat the word') ->describe('--upper', 'Converts the result to uppercase'); } protected function execute() { $result = str_repeat($this->args->word, $this->args->count); if ($this->option('--upper')) $result = strtoupper($result); $this->console->line($result); } }
我们使用syntax()方法来定义参数的语法。传递给此方法的字符串遵循此处描述的规则
describe()方法用于描述一个参数。
当你定义命令的语法时,参数会自动解析,并在execute()方法中通过args属性可用。
help子命令显示参数和选项的完整描述
结果是
$ php repeat.php foo 5
foofoofoofoofoo
$ php repeat.php bar --upper
BARBARBAR
在第二个例子中,count参数自动取其默认值。
警告:提供错误的参数将生成错误
交互式读取参数和选项
一些命令可能有长而复杂的参数列表。由于Syntax库的存在,定义此类命令的语法很容易,但使用命令行输入参数则变得具有挑战性。
让我们以以下命令为例
class ClassGenerator extends Command { protected function init() { $this->name('Class Generator') ->version('1.0.0') ->description('Generates basic code for a class.') ->syntax(' language: string, name: string, parents: ([string]:[]), interfaces: ([string]:[]), attrs: [{ name, type, hasGetter: (boolean:true), hasSetter: (boolean:true), isStatic: (boolean:false) }], methods: ([{ name: string, type: string, args: [{ name, type, default: (string:null) |.}], isStatic: (boolean:false) }]:[]) ') ->descriptions([ 'language' => 'The programming language in which the code will be generated.', 'name' => 'The name of the class.', 'parents' => 'List of parent classes names.', 'interfaces' => 'List of implemented interfaces.', 'attrs' => 'List of attributes of the class.', 'attrs.name' => 'The name of the attribute.', 'attrs.type' => 'The type of the attribute.', 'attrs.hasGetter' => 'Generate a getter for the attribute.', 'attrs.hasSetter' => 'Generate a setter for the attribute.', 'attrs.isStatic' => 'The attribute is static.', 'methods' => 'List of methods of the class.', 'methods.name' => 'The method name.', 'methods.type' => 'The method return type.', 'methods.args' => 'List of arguments of the method.', 'methods.isStatic' => 'This method is static.' ]); } protected function execute() { $this->console->line("Generate code for the class {$this->args->name} in {$this->args->language}..."); } }
如果你使用-i标志运行命令,它将允许你交互式地输入参数
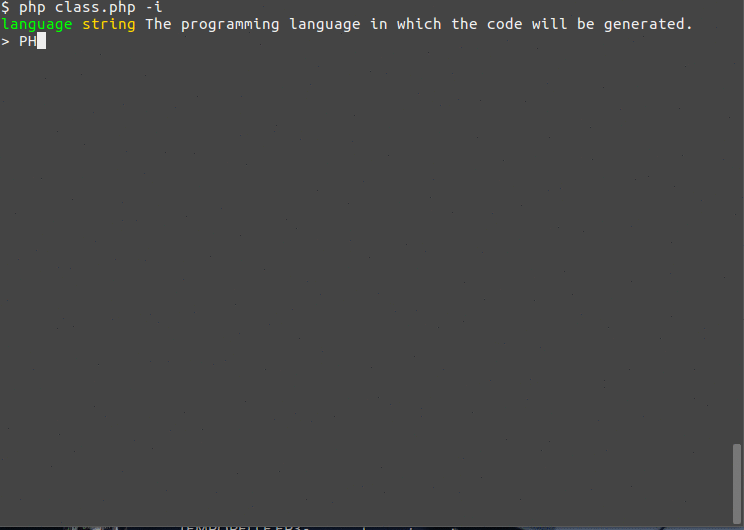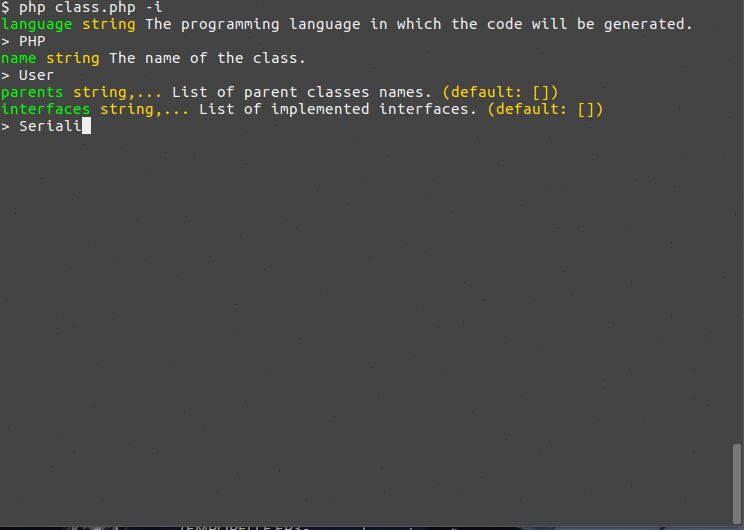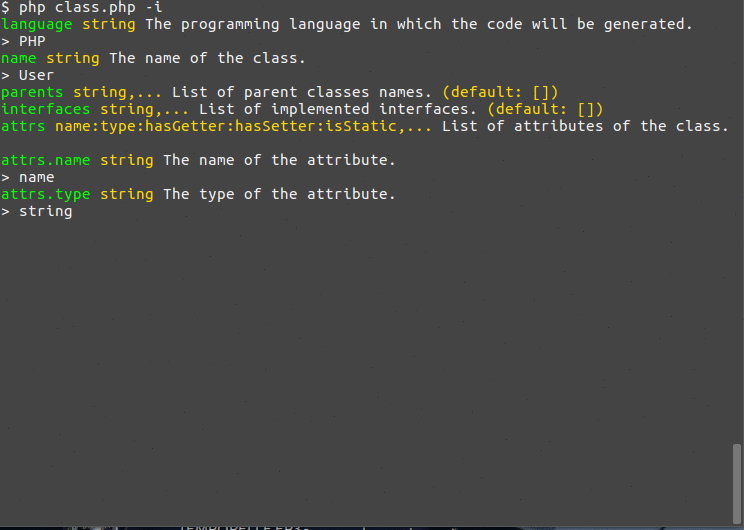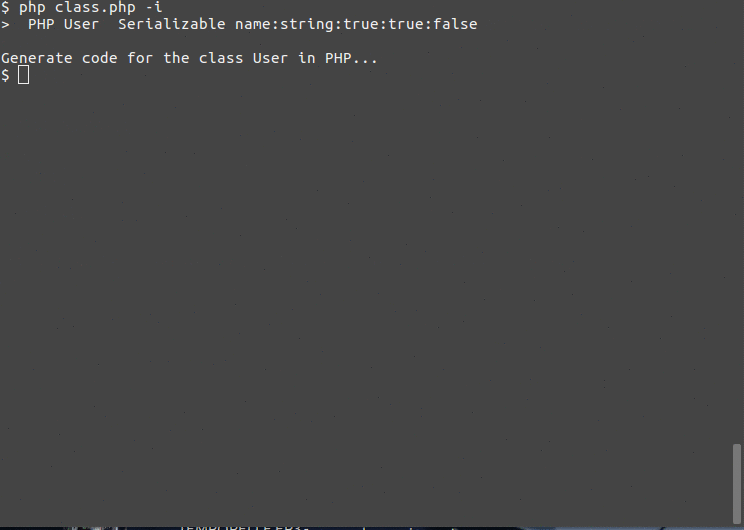
读取所有参数后,命令将显示输入参数的命令行版本
> PHP User Serializable name:string:true:true:false
这意味着运行
$ php class.php PHP User Serializable name:string:true:true:false
会产生相同的结果。
处理文件系统
fs属性是Tarsana\IO\Filesystem的一个实例,你可以用它来处理文件和目录。阅读文档以了解完整的API。
默认情况下,Filesystem实例指向运行命令的目录。你还可以将其初始化为你想要的任何目录
using Tarsana\IO\Filesystem; // ... protected function init() { $this->fs(new Filesystem('path/to/directory/you/want')); }
加载配置
除了命令行参数之外,用户还可以通过配置文件向您的命令提供数据。这很有用,因为它允许你定义一个默认的配置文件,并允许用户通过自定义配置文件更改一些值。
让我们写一个示例命令,它有一个全局配置文件在/home/user/.config.json。它允许用户通过当前目录中的config.json文件自定义值
class ConfigCommand extends Command { protected function init() { // ... $this->configPaths(['/home/user/.config.json', 'config.json']); } protected function execute() { // getting a config value // assuming that $data is the merged content of the config files $this->config('name'); // returns $data['name'] $this->config('foo.bar.baz'); // returns $data['foo']['bar']['baz'] $this->config(); // returns $data } }
-
configPaths方法接受一个路径列表,加载它们并将它们合并到一个配置中(它内部使用array_replace_recursive)。 -
config方法用于检索配置值。
注意
-
目前仅支持
json文件作为配置文件。请提交一个问题或发起一个拉取请求以添加其他格式。 -
configPaths将静默忽略在文件系统中不存在的路径。 -
子命令将始终具有与其父命令相同的配置数据,除非使用
configPaths覆盖它。
渲染模板
Command类还提供了渲染模板的可能性。默认的模板引擎是Twig,但你可以通过实现TemplateLoaderInterface和TemplateInterface接口来使用你喜欢的任何模板引擎。
让我们创建一个渲染简单模板的命令。为此,我们将创建两个文件
render-hello.php
templates/
hello.twig
hello.twig
Hello {{name}}
这是一个简单的模板,打印一个问候消息。
render-hello.php
<?php require __DIR__.'vendor/autoload.php'; use Tarsana\Command\Command; use Tarsana\Command\Templates\TwigTemplateLoader; class RenderHelloCommand extends Command { protected function init () { $this ->name('Renders Simple Template') ->description('Renders a simple twig template') ->syntax('name: (string:You)') ->describe('name', 'Your name') ->templatesPath(__DIR__.'/templates'); // defines the path to the templates } protected function execute() { $message = $this->template('hello') ->render([ 'name' => $this->args->name ]); $this->console->line($message); } } (new RenderHelloCommand)->run();
结果
$ php render-hello.php Foo
Hello Foo
$ php render-hello.php
Hello You
添加子命令
你可以在初始化命令时添加子命令。
// ... protected function init() { //... // Assuming that FooCommand and BarCommand are already defined $this->command('foo', new FooCommand) ->command('bar', new BarCommand); // this erases the subcommand with key 'bar' if exists // Or set all subcommands at once (this will erase any previous subcommands) $this->commands([ 'foo' => new FooCommand, 'bar' => new BarCommand ]); // Later on you can get subcommands $this->commands(); // returns all the subcommands as key-value array $this->command('name'); // gets the subcommand with the given name // will throw an exception if the subcommand is missing $this->hasCommand('name'); // checks if a subcommand with the given name exists }
现在,当你运行
$ php your-script.php foo other arguments here
时,FooCommand将以other arguments here作为参数运行。
注意:子命令将始终具有指向其父对象相同的console、fs和templatesLoader属性的属性,只要你不在子命令的代码中明确更改它们。
测试命令
类Tarsana\Tester\CommandTestCase扩展了PHPUnit\Framework\TestCase并为测试Tarsana命令添加了有用的方法。
测试输入和输出
让我们为上面的HelloWorld命令编写一个测试,该命令读取用户名并显示问候信息。
use Tarsana\Tester\CommandTestCase; class HelloWorldTest extends CommandTestCase { public function test_it_prints_hello() { $this->withStdin("Amine\n") ->command(new HelloWorld) ->prints("Your name:") ->prints("Hello Amine<br>"); } public function test_it_shows_hello_world_version() { $this->command(new HelloWorld, ['--version']) ->printsExactly("<info>Hello World</info> version <info>1.0.0-alpha</info><br>"); } }
withStdin(string $content) : CommandTestCase;
设置命令的标准输入的内容。
command(Command $c, array $args = []) : CommandTestCase;
使用标准输入和$args运行命令$c,然后存储其输出以供进一步断言。
printsExactly(string $text) : CommandTestCase; prints(string $text) : CommandTestCase; printsError(string $text) : CommandTestCase;
-
printsExactly断言命令的标准输出等于$text。注意,为了便于测试,标签不会被应用。 -
prints断言命令的标准输出包含$text。 -
printsError断言命令的错误输出包含$text。
测试参数和选项
现在让我们测试上面的RepeatCommand。
class RepeatCommandTest extends CommandTestCase { public function test_it_repeats_word_three_times() { $this->command(new RepeatCommand, ['foo']) ->argsEqual((object) [ 'word' => 'foo', 'count' => 3 ]) ->optionsEqual([ '--upper' => false ]) ->printsExactly("foofoofoo<br>"); } public function test_it_repeats_word_n_times_uppercase() { $this->command(new RepeatCommand, ['bar', '5', '--upper']) ->argsEqual((object) [ 'word' => 'bar', 'count' => 5 ]) ->optionsEqual([ '--upper' => true ]) ->printsExactly("BARBARBARBARBAR<br>"); } }
argsEqual(object $args) : CommandTestCase; optionsEqual(array $options) : CommandTestCase;
断言命令解析的参数和选项等于给定的值。
测试文件系统
让我们考虑以下命令
class ListCommand extends Command { protected function init () { $this->name('List') ->version('1.0.0-alpha') ->description('Lists files and directories in the current directory.'); } protected function execute() { foreach($this->fs->find('*')->asArray() as $file) { $this->console->line($file->name()); } } }
测试可以写成如下形式
class ListCommandTest extends CommandTestCase { public function test_it_lists_files_and_directories() { $this->havingFile('demo.txt', 'Some text here!') ->havingFile('doc.pdf') ->havingDir('src') ->command(new ListCommand) ->printsExactly('demo.txt<br>doc.pdf<br>src<br>'); } public function test_it_prints_nothing_when_no_files() { $this->command(new ListCommand) ->printsExactly(''); } }
havingFile(string $path, string $content = '') : CommandTestCase; havingDir(string $path) : CommandTestCase;
CommandTestCase使用虚拟文件系统运行命令。在运行命令之前,可以使用方法havingFile和havingDir在该文件系统上创建文件和目录。
下一步
请查看examples目录中的示例,并尝试使用库构建一些出色的命令。任何反馈都受欢迎!
开发笔记
-
版本 2.0.0 Tarsana命令现在使用PHPUnit 9,因此需要PHP 7.3或PHP 7.4。
-
版本 1.2.1
CommandTestCase现在是一个抽象类,以避免PHPUnit警告。 -
版本 1.2.0 命令现在可以从多个JSON文件中加载配置。
-
版本 1.1.1 修复了子命令没有默认的
--help、--version和-i子命令的bug。 -
版本 1.1.0 将标志
-i添加到命令中,以启用交互式读取参数和选项。 -
版本 1.0.1 修复了子命令具有与其父对象不同的
fs和templatesLoader实例的bug。 -
版本 1.0.0 首个版本终于发布;祝您玩得开心!