nti / sync-bundle
Symfony NTISyncBundle
Requires
- symfony/serializer: >=2.0
README
安装
-
使用 composer 安装包
$ composer require nti/sync-bundle "dev-master" -
将包配置添加到 AppKernel
public function registerBundles() { $bundles = array( ... new NTI\SyncBundle\NTISyncBundle(), ... ); } -
更新数据库模式
$ php app/console doctrine:schema:update -
将路由添加到
routing.yml... nti_sync: resource: "@NTISyncBundle/Resources/config/routing.yml"
要求
以下是在实现此包时需要考虑的事项列表
- 在同步过程中需要考虑的任何实体必须在类级别有
@NTI\SyncEntity注解。 - 应该更改其父实体最后同步时间戳的
ManyToOne关系应使用注解@NTI\SyncParent(getter="[Getter Name]")(更多信息请参阅下面的示例)。 - 需要同步的实体必须有一个实现了
SyncRepositoryInterface的存储库(更多信息请参阅以下内容)。 - 对于每个实体,需要配置
SyncMapping映射,因为它是查找时用作参考的列表。 - 对于每个映射,应该创建
SyncState。这可以在创建所有SyncMapping之后通过此查询来完成`INSERT INTO nti_sync_state(mapping_id, timestamp) SELECT id, 0 FROM sync_nti_mapping;` - 如果实体将要从客户端同步,则必须在
SyncMapping数据库条目中定义一个服务。此外,此方法需要实现SyncServiceInterface接口。
跟踪更改
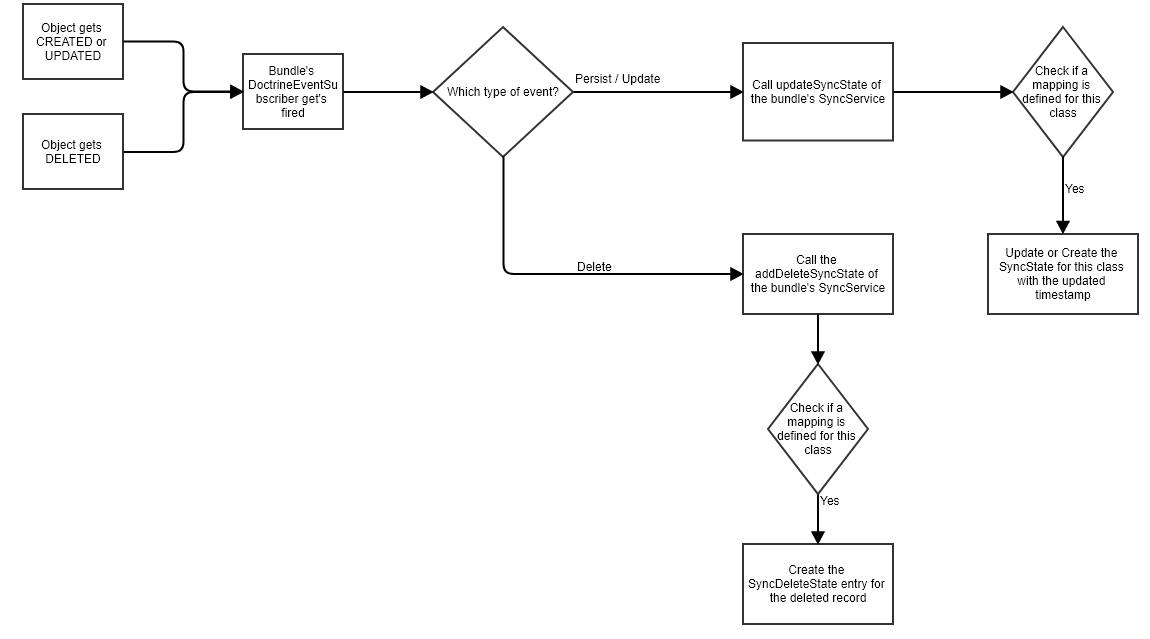
此包跟踪同步中更改的方式如下
- 该包有一个
DoctrineEventListener监听onFlush事件。 - 事件被触发后,包将抓取每个带有
@NTI\SyncEntity注解的实体。 - 如果实体有定义的
SyncMapping,则系统将此映射的last_timestamp字段更新为当前time()。 - 如果实体有一个名为
setLastTimestamp()的方法,则将使用time()作为参数调用它,并重新计算或计算更改。 - 将检查实体的所有属性,以查找包含注解
@NTI\SyncParent(getter="[Getter Name]")的属性。如果找到,将调用获取器,如果结果是具有@NTI\SyncEntity的对象,则从点 #3 开始再次处理。此过程是递归的。
配置
以下是包的默认配置。如果您需要修改默认值,请将其放在您的 config.yml 中
nti_sync: deletes: # Identifier to use when an item gets deleted. This would go in your `deletes` section as shown below identifier_getter: "getId"
类示例
```
<?php
...
use NTI\Annotations as NTI;
/**
* ...
* @NTI\SyncEntity()
*/
public class Product {
...
/**
* @ORM\Column(name="last_timestamp", type="bigint", options={"default": 0})
*/
private $lastTimestamp;
...
/**
* Set lastTimestamp
* @param $lastTimestamp
* @return Company
*/
public function setLastTimestamp($lastTimestamp)
{
$this->lastTimestamp = $lastTimestamp;
return $this;
}
/**
* Get lastTimestamp
* @return integer
*/
public function getLastTimestamp()
{
return $this->lastTimestamp;
}
}
以下是一个使用 ManyToOne 的类的示例,其中子实体还需要更新父实体的 last_timestamp
```
<?php
...
use NTI\Annotations as NTI;
/**
* ...
* @NTI\SyncEntity()
*/
public class ProductChild {
...
/**
* @NTI\SyncParent(getter="getProduct")
* @ORM\ManyToOne(targetEntity="AppBundle\Entity\Product\Product")
*/
private $product;
...
/**
* Get Product
* @return Product
*/
public function getProduct()
{
return $this->product;
}
}
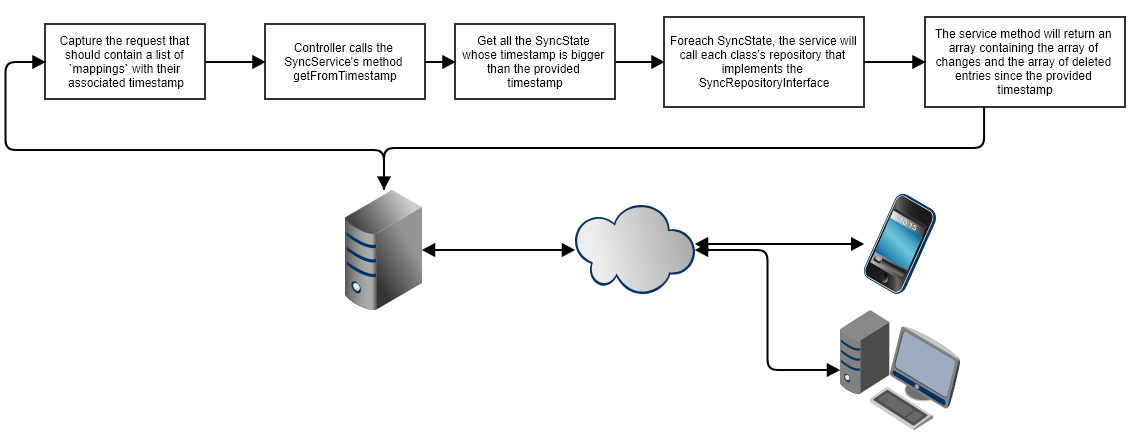
以下是包跟踪同步状态的一般过程
以下是客户端在特定时间戳后请求更改时发生的一般过程
实现(拉取)
同步过程背后的想法是,将要同步的每个对象都应在其实体存储库中实现 SyncRepositoryInterface。
/**
* Interface SyncRepositoryInterface
* @package NTI\SyncBundle\Interfaces
*/
interface SyncRepositoryInterface {
/**
* This function should return a plain array containing the results to be sent to the client
* when a sync is requested. The container is also passed as a parameter in order to give additional
* flexibility to the repository when making decision on what to show to the client. For example, if the user
* making the request only has access to a portion of the data, this can be handled via the container in this method
* of the repository.
*
* Note 1: If the `updatedOn` of a child entity is the one that is affected and not the parent, you may have to take that
* into account when doing your queries so that the updated information shows up in the results if desired when doing
* the comparison with the timestamp
*
* For example:
*
* $qb -> ...
* $qb -> leftJoin('a.b', 'b')
* $qb -> andWhere($qb->expr()->orX(
* $qb->expr()->gte('a.lastTimestamp', $date),
* $qb->expr()->gte('b.lastTimestamp', $date)
* ))
* ...
*
* This way if the only way of syncronizing B is through A, next time A gets synched B changes will be reflected.
*
* The resulting structure should be the following:
*
* array(
* "data" => (array of objects),
* SyncState::REAL_LAST_TIMESTAMP => (last updated_on date from the array of objects),
* )
*
*
* @param $timestamp
* @param ContainerInterface $container
* @param array $serializationGroups
* @return mixed
*/
public function findFromTimestamp($timestamp, ContainerInterface $container, $serializationGroups = array());
除了实现接口之外,在数据库 nti_sync_mapping 中还应配置将要同步的每个类的映射以及名称。
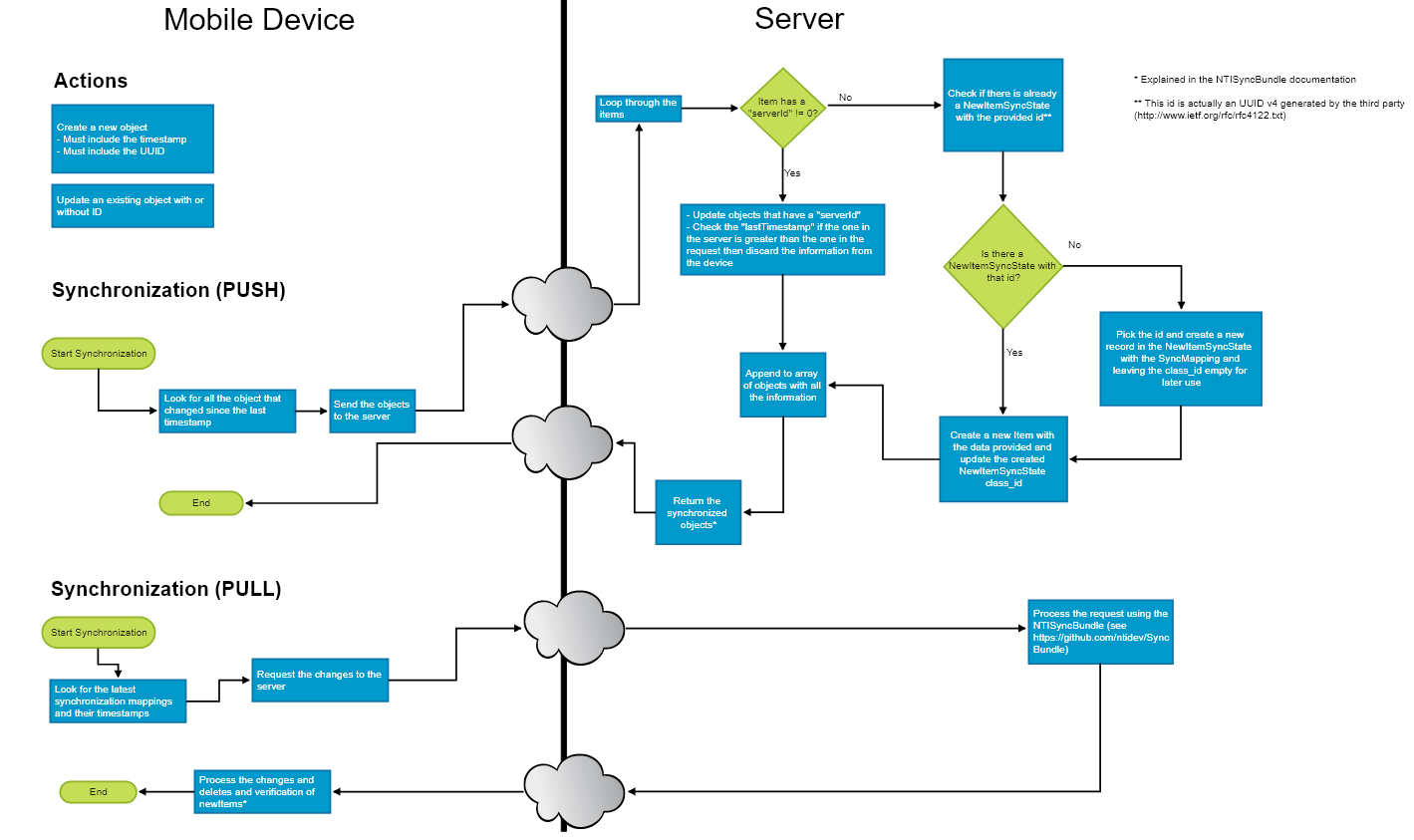
首先,想法是从服务器获取更改和映射的摘要
GET /nti/sync/summary
服务器将响应以下结构
[
{
"id": 1,
"mapping": {
"id": 1,
"name": "Product",
"class": "AppBundle\\Entity\\Product\\Product",
"sync_service": "AppBundle\\Service\\Product\\ProductService"
},
"timestamp": 1515076764
},
...
]
响应包含一组映射及其最后注册的时间戳。这个时间戳可以在同步过程中用来确定哪些内容已更改以及需要同步什么。
然后,第三方使用以下结构向服务器发起请求
POST /nti/sync/pull
Content-Type: application/json
{
"mappings": [
{ "mapping": "[MAPPING_NAME]", "timestamp": [LAST_TIMESTAMP_CHECKED] }
]
}
收到请求后,如果存在指定名称的映射,系统将调用存储库的findFromTimestamp实现,并返回以下结果(以产品实体为例)
{
"[MAPPING_NAME]": {
"changes": [
{
"id": 2,
"productId": "POTATOBAG",
"name": "Potato bag",
"description": "Bag of potatoes",
"price": "32.99",
"cost": "0",
"createdOn": "11/30/2017 04:22:49 PM",
"updatedOn": "11/30/2017 04:22:49 PM",
"lastTimestamp": 1515068439
},
...
],
"newItems": [
{
"id": 1,
"uuid": "24a7aff0-fea8-4f62-b421-6f97f464f310",
"mapping": {
"id": 1,
"name": "Product",
"class": "AppBundle\\Entity\\Product\\Product",
"sync_service": "AppBundle\\Service\\Product\\ProductService"
},
"class_id": 8,
"timestamp": 1515068439
},
...
],
"deletes": [
{
"id": 2,
"mapping": {
"id": 2,
"name": "Product",
"class": "AppBundle\\Entity\\Product\\Product"
},
"classId": "[identifier_getter result]",
"timestamp": 1512080746
},
...
],
"failedItems": [
{
"id": 7,
"uuid": "abcdefg-123456-hifgxyz-78901",
"mapping": {
"id": 9,
"name": "Product",
"class": "AppBundle\\Entity\\Product\\Product",
"sync_service": " ... "
},
"classId": 137,
"timestamp": 1512080747,
"errors": [...errors provided...]
},
...
],
"_real_last_timestamp": 1512092445
}
}
服务器将返回 changes、newItems、failedItems 和 deletes。其中 changes 将包含存储库的 SyncRepositoryInterface 实现返回数组的 data 部分。deletes 将包含自指定时间戳以来记录的 SyncDeleteState 列表。newItems 将包含 SyncNewItemState 列表,表示自提供的时间戳以来创建的新项,包括当时给出的 UUID(这对于第三方设备在首次拉取信息时很有帮助,它们可以验证一个项目是否已经创建,但它们在本地存储中没有该项目的 ID,从而避免在服务器上创建重复项)。failedItems 将包含 SyncFailedItemState 列表,列表中的每个项目都包含一个具有找到的错误 errors 属性的 errors 属性。
应该使用 _real_last_timestamp,因为它可以帮助对全量同步的结果进行分页,并帮助客户端获取响应中最后一个对象的实际最后时间戳。这需要在存储库中获取,可以通过简单地从存储库的结果中获取最后一项并调用 getLastTimestamp() 来完成。
从这一点开始,客户端必须跟踪 _real_last_timestamp 以便将来执行同步。
实现(推送)
以下是推送/拉取过程的一般思路
服务器端
对于每个映射的实体 SyncMapping,应指定一个服务。该服务必须实现 SyncServiceInterface。
客户端
为了处理第三方设备的推送,它必须在请求中提供以下结构
POST /nti/sync/push
Content-Type: application/json
{
"mappings": [
{ "mapping": "[MAPPING_NAME]", "data": [
{
"id": "5eb86d4a-9b82-42f3-abae-82b1b61ad58e",
"serverId": 1,
"name": "Product1",
"description": "Description of the product",
"price": 55,
"lastTimestamp": 1512080746
},
...
] }
]
}
当服务器接收到此请求时,它将执行相应 SyncMapping 中配置服务的 sync() 方法,并传递该参数的数据数组。您的 sync() 函数需要操作此信息,并返回一个数组,该数组将被包含在响应中,对应于相应的映射名称。
然后,服务器返回以下结构
{
"mappings": [
{ "[MAPPING_NAME]": "RESULT OF YOUR sync() HERE" },
{ "[MAPPING_NAME]": "RESULT OF YOUR sync() HERE" },
{ "[MAPPING_NAME]": "RESULT OF YOUR sync() HERE" },
]
}
待办事项
- 处理第三方删除
ManyToMany关系很复杂,可能会导致性能问题