miowng / laravel-eloquent-join
此包引入了eloquent模型和关系的连接魔法。
Requires
- illuminate/database: ^5.5|^6.0|^7.0|^8.0
Requires (Dev)
- dev-master
- 4.2
- 4.1.3
- 4.1.2
- 4.1.1
- 4.1.0
- 4.0.9
- 4.0.8
- 4.0.7
- 4.0.6
- 4.0.5
- 4.0.4
- 4.0.3
- 4.0.2
- 4.0.1
- 4.0.0
- 3.0.2
- 3.0.1
- 3.0.0
- 2.2.4
- 2.1.x-dev
- 2.1.4
- 2.1.3
- 2.1.2
- 2.1.0
- 2.0.x-dev
- 2.0.4
- 2.0.3
- 2.0.2
- 2.0.0
- 1.3.x-dev
- 1.3.4
- 1.3.3
- 1.3.2
- 1.3.0
- 1.2.x-dev
- 1.2.4
- 1.2.3
- 1.2.2
- 1.2.1
- 1.2.0
- dev-filip-patch-5
- dev-filip-patch3
- dev-filip-patch2
- dev-filip-patch
This package is auto-updated.
Last update: 2024-09-18 14:31:23 UTC
README
Laravel Eloquent Join
此包引入了eloquent模型和关系的连接魔法。
简介
Eloquent是一个非常强大的ORM,但其连接能力非常有限。
第一个Eloquent问题(排序)
使用laravel,你无法在不手动连接相关表的情况下对关系字段进行排序,这非常尴尬。让我给你几个原因。如果你有一个包含<强>posts和相关<强>categories的表,你的代码可能看起来像这样
$posts = Post::select('posts.*')
->join('categories', 'categories.id', '=', 'posts.category_id')
->groupBy('posts.id')
->where('categories.deleted_at', '=', null)
->orderBy('categories.name');
if(request()->get('date')){
$posts->where('posts.date', $date)
}
$posts = $posts->get();
1.第一个问题是你需要担心选择。
->select('posts.*')
原因:没有从类别中<强>选择id,它可以被选中并注入到Post模型中。
2.第二个问题是你需要担心<强>groupBy。
->groupBy('posts.id');
原因:如果关系是HasOne,并且对于文章有多个类别,查询将返回更多行。
3.第三个问题是你需要将所有其他where子句从
->where('date', $date)
改为
->where('posts.date', $date)
原因:一个<强>post和一个<强>category可以有一个“日期”属性,在这种情况下,如果没有选择具有表名称的属性,将抛出“模糊列”错误。
4.第四个问题是你在使用表名(不是模型),这也是不好的,也很尴尬。
->where('posts.date', $date)
5.第五个问题是你需要担心连接表的软删除。如果<强>category使用了SoftDeletes特性,你必须添加
->where('categories.deleted_at', '=', null)
这个包将为你解决所有上述问题。与<强>排序不同,你可以不连接相关表就执行关系字段的<强>过滤,但这个包将让你更容易做到这一点。
第二个Eloquent问题(子查询)
使用laravel,你可以对关系属性执行where,但laravel将生成比连接更慢的子查询。使用这个包,你将能够以优雅的方式使用连接执行关系上的where。
要求
包还针对SQLite、MySql和PostgreSql进行了测试
安装与设置
1.使用composer安装包
composer require fico7489/laravel-eloquent-join
使用这个语句,composer将为你当前的laravel版本安装最高可用的包版本。
2.在你的基模型或特定模型中使用Fico7489\Laravel\EloquentJoin\Traits\EloquentJoinTrait特性。
...
use Fico7489\Laravel\EloquentJoin\Traits\EloquentJoin;
use Illuminate\Database\Eloquent\Model;
abstract class BaseModel extends Model
{
use EloquentJoin;
...
3.重要
对于<强>MySql,请确保<强>strict配置设置为<强>false
config/database.php
'mysql' => [
...
'strict' => false,
...
就这样,你就可以开始了。
选项
选项可以在模型中设置
class Seller extends BaseModel
{
protected $useTableAlias = false;
protected $appendRelationsCount = false;
protected $leftJoin = false;
protected $aggregateMethod = 'MAX';
或在查询中设置
Order::setUseTableAlias(true)->get();
Order::setAppendRelationsCount(true)->get();
Order::setLeftJoin(true)->get();
Order::setAggregateMethod(true)->get();
useTableAlias
是否应该为连接表使用别名(默认=false)
如果设置为<强>true,查询将如下所示
select "sellers".* from "sellers"
left join "locations" as "5b5c093d2e00f"
...
如果设置为<强>false,查询将如下所示
select "sellers".*
from "sellers"
left join "locations"
...
别名是一个随机生成的字符串。
appendRelationsCount
是否应该自动将关系计数字段附加到结果中(默认=false)
如果设置为<强>true,查询将如下所示
select "sellers".*, count(locations.id) AS locations_count
from "sellers"
left join "locations" as "5b5c093d2e00f"
...
每个<强>关系都通过下划线连接,并在末尾添加前缀<强>_count。例如,对于
->joinRelations('seller.locations')
字段将是<强>seller_locations_count
leftJoin
是否应该使用<强>inner join或<强>left join(默认=true)
select "sellers".*
from "sellers"
inner join "locations"
...
vs
select "sellers".*
from "sellers"
left join "locations"
...
aggregateMethod
使用哪个聚合方法进行排序(默认='MAX')。
当在连接表上执行连接时,我们必须在排序字段上应用聚合函数,以便我们可以应用group by子句并防止结果重复。
select "sellers".*, MAX("locations" ."number") AS sort
from "sellers"
left join "locations"
group by "locations" ."id"
order by sort
...
选项有:<强>SUM、<强>AVG、<强>MAX、<强>MIN、<强>COUNT
用法
当前可用的用于连接查询的关系
- 属于
- 有一个
- 有多个
为 BelongsTo 和 HasOne 关系新增的优雅构建器子句
joinRelations($relations, $leftJoin = null)
- $relations 要连接的关系
- $leftJoin 使用 左连接 或 内连接,默认 左连接
orderByJoin($column, $direction = 'asc', $aggregateMethod = null)
- $column 和 $direction 参数与默认 eloquent orderBy() 相同
- $aggregateMethod 参数定义要使用的聚合方法(SUM、AVG、MAX、MIN、COUNT),默认 MAX
whereJoin($column, $operator, $value, $boolean = 'and')
- 参数与默认 eloquent where() 相同
orWhereJoin($column, $operator, $value)
- 参数与默认 eloquent orWhere() 相同
whereInJoin($column, $values, $boolean = 'and', $not = false)
- 参数与默认 eloquent whereIn() 相同
whereNotInJoin($column, $values, $boolean = 'and')
- 参数与默认 eloquent whereNotIn() 相同
orWhereInJoin($column, $values)
- 参数与默认 eloquent orWhereIn() 相同
orWhereNotInJoin($column, $values)
- 参数与默认 eloquent orWhereNotIn() 相同
可以在 BelongsTo、HasOne 和 HasMany 关系上使用连接子句的允许子句
- 用于连接查询的想要使用的关系只能有这些子句:where、orWhere、withTrashed、onlyTrashed、withoutTrashed。
- 子句 where 和 orWhere 只能有以下变体 ** ->where($column, $operator, $value) ** ->where([$column => $value])
- 不允许使用闭包。
- 不允许使用其他子句如 whereHas、orderBy 等。
- 您可以在关系中添加不允许的子句并以 eloquent 的正常方式使用它们,但在这些情况下,您不能使用这些关系进行连接查询。
允许的关系
public function locationPrimary()
{
return $this->hasOne(Location::class)
->where('is_primary', '=', 1)
->orWhere('is_primary', '=', 1)
->withTrashed();
}
不允许的关系
public function locationPrimary()
{
return $this->hasOne(Location::class)
->where('is_primary', '=', 1)
->orWhere('is_primary', '=', 1)
->withTrashed()
->whereHas('state', function($query){return $query;}
->orderBy('name')
->where(function($query){
return $query->where('is_primary', '=', 1);
});
}
不允许第二个关系的原因是,这个包应该在连接子句上应用所有这些子句,eloquent 使用子查询独立应用这些子句(而不是在连接子句上),这样做更简单。
您可能会觉得规则和限制太多,但实际上并非如此。请放心,如果您创建了不允许的查询,将会抛出适当的异常,您将会知道发生了什么。
其他
- 如果模型使用了 SoftDelete 特性,则会自动应用 where deleted_at != null
- 您可以无限次地组合新子句
- 如果您在相同的关系上多次组合子句,包将只连接相关表一次
Seller::whereJoin('city.title', '=', 'test')
->orWhereJoin('city.title', '=', 'test2');
- 您可以在闭包中调用新子句
Seller::where(function ($query) {
$query
->whereJoin('city.title', '=', 'test')
->orWhereJoin('city.title', '=', 'test2');
});
- 您可以组合连接子句,例如 whereJoin(),与 eloquent 子句,例如 orderBy()
Seller::whereJoin('title', '=', 'test')
->whereJoin('city.title', '=', 'test')
->orderByJoin('city.title')
->get();
请参阅真实示例中的操作
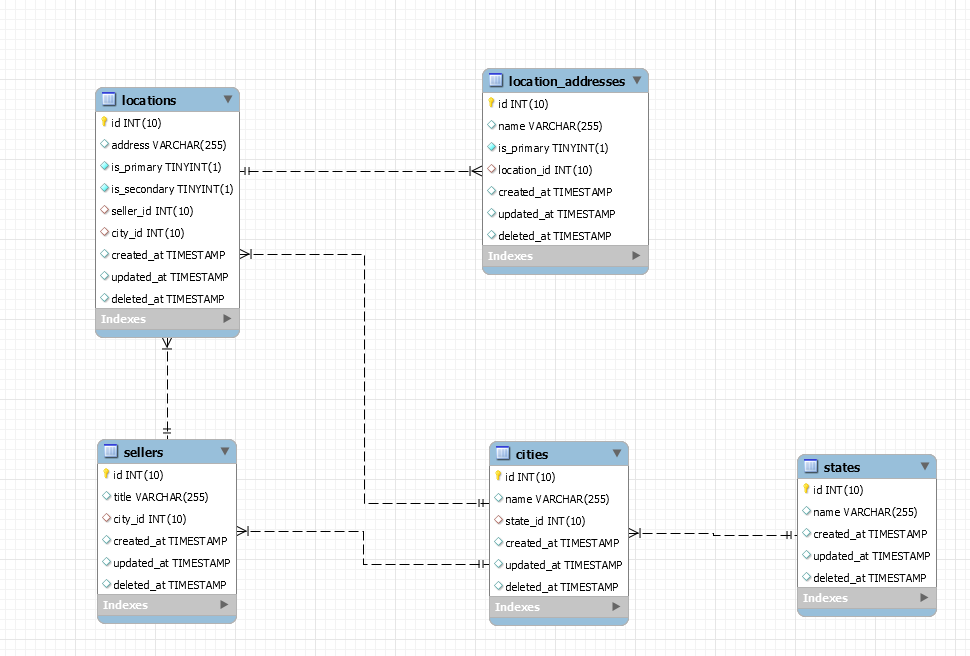
数据库模式
模型
class Seller extends BaseModel
{
public function locations()
{
return $this->hasMany(Location::class);
}
public function locationPrimary()
{
return $this->hasOne(Location::class)
->where('is_primary', '=', 1);
}
public function city()
{
return $this->belongsTo(City::class);
}
class Location extends BaseModel
{
public function locationAddressPrimary()
{
return $this->hasOne(LocationAddress::class)
->where('is_primary', '=', 1);
}
class City extends BaseModel
{
public function state()
{
return $this->belongsTo(State::class);
}
}
连接
连接 BelongsTo
Seller::joinRelations('city')
连接 HasOne
Seller::joinRelations('locationPrimary')
连接 HasMany
Seller::joinRelations('locations')
连接混合
Seller::joinRelations('city.state')
连接(混合左连接)
Seller::joinRelations('city', true)->joinRelations('city.state', false)
连接(多个关系)
Seller::join(['city.state', 'locations'])
排序
排序 BelongsTo
Seller::orderByJoin('city.title')
排序 HasOne
Seller::orderByJoin('locationPrimary.address')
排序 HasMany
Seller::orderByJoin('locations.title')
排序 混合
Seller::orderByJoin('city.state.title')
排序(带有聚合函数的特殊情况)
按关系计数排序
Seller::orderByJoin('locations.id', 'asc', 'COUNT')
按关系字段 SUM 排序
Seller::orderByJoin('locations.is_primary', 'asc', 'SUM')
按关系字段 AVG 排序
Seller::orderByJoin('locations.is_primary', 'asc', 'AVG')
按关系字段 MAX 排序
Seller::orderByJoin('locations.is_primary', 'asc', 'MAX')
按关系字段 MIN 排序
卖家::按顺序连接('locations.is_primary', 'asc', 'MIN')
过滤(where 或 orWhere)
过滤属于
卖家::whereJoin('city.title', '=', 'test')
过滤一对一
卖家::whereJoin('locationPrimary.address', '=', 'test')
过滤多对多
卖家::whereJoin('locations.title', '=', 'test')
混合过滤
卖家::whereJoin('city.state.title', '=', 'test')
关系计数
$sellers = Seller::setAppendRelationsCount(true)->join('locations', '=', 'test')
->get();
foreach ($sellers as $seller){
echo 'Number of location = ' . $seller->locations_count;
}
过滤(混合左连接)
Seller::joinRelations('city', true)
->joinRelations('city.state', false)
->whereJoin('city.id', '=', 1)
->orWhereJoin('city.state.id', '=', 1)
生成的查询
查询
Order::whereJoin('seller.id', '=', 1)->get();
SQL
select "orders".*
from "orders"
left join "sellers" on "sellers"."id" = "orders"."seller_id"
where "sellers"."id" = ?
and "orders"."deleted_at" is null
group by "orders"."id"
查询
Order::orderByJoin('seller.id', '=', 1)->get();
SQL
select "orders".*, MAX(sellers.id) as sort
from "orders"
left join "sellers" on "sellers"."id" = "orders"."seller_id"
where "orders"."deleted_at" is null
group by "orders"."id"
order by sort asc
包的优雅性
让我们看看文档中的第一个示例现在是什么样子。这段代码
$posts = Post::select('posts.*')
->join('categories', 'categories.id', '=', 'posts.category_id')
->groupBy('posts.id')
->where('categories.deleted_at', '=', null)
->orderBy('categories.name');
if(request()->get('date')){
$posts->where('date', $date)
}
$posts = $posts->get();
现在是
$posts = Post::orderByJoin('category.name');
if(request()->get('date')){
$posts->where('posts.date', $date)
}
$posts = $posts->get();
这两个片段执行相同的功能。
测试
此包经过良好的测试。如果您想运行测试,只需运行 composer update,然后使用 "vendor/bin/phpunit" 运行测试。
贡献
请随意创建关于
- 错误
- 注意事项
- 请求新功能
- 问题
- 澄清
- 等等...
许可
MIT
自由软件,太棒了!